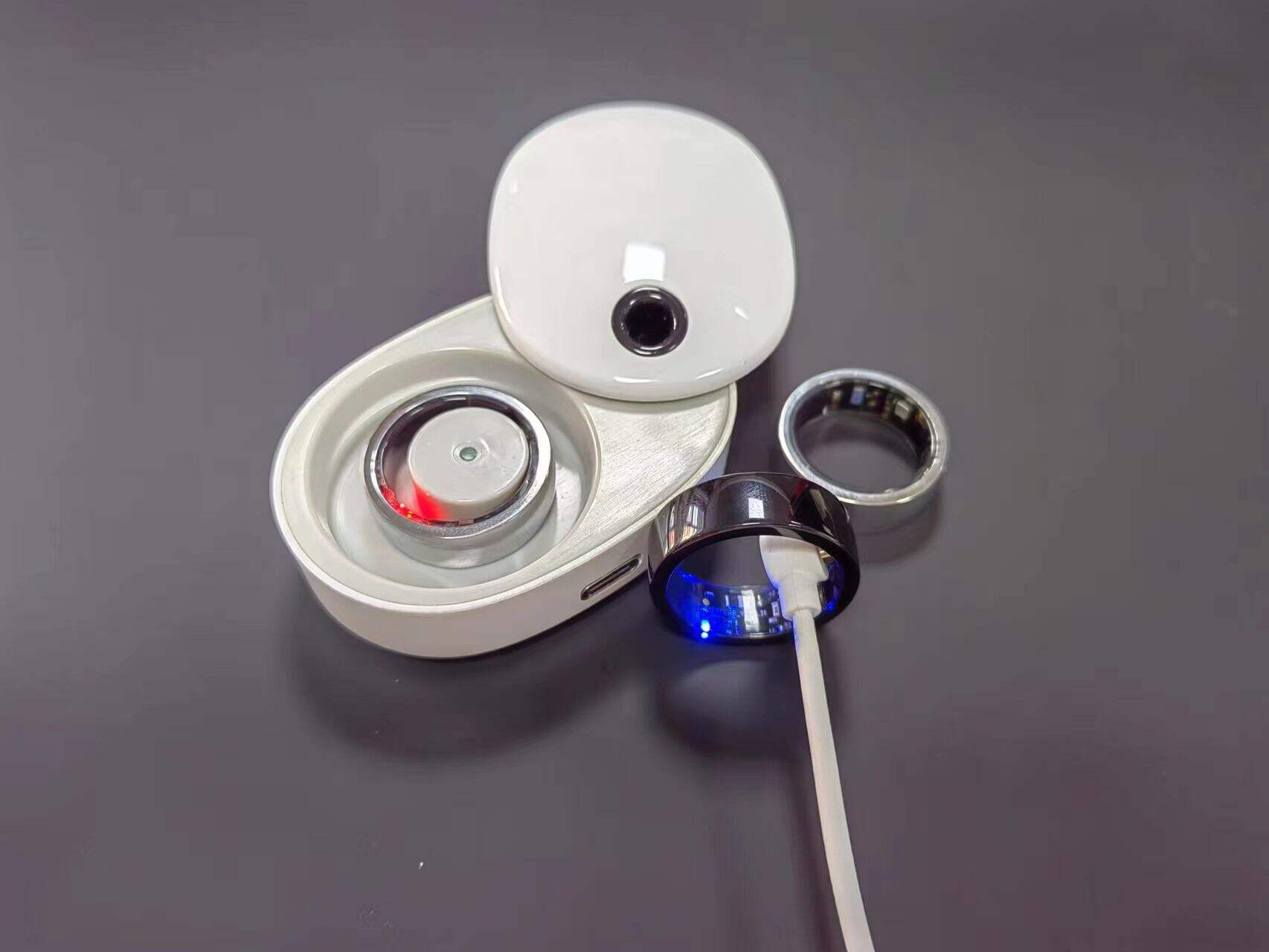
What Is a Pogopin and Why Is It Used in Precision Electronic Connections?
A pogopin represents one of the most ingenious solutions in modern electronics, providing reliable temporary connections between circuit boards and testing equipment. This spring-loaded connector has revolutionized how engineers approach electrical testing, charging systems, and modular electronic designs. Understanding what a pogopin is and how it functions opens up possibilities for creating more efficient, durable, and cost-effective electronic products across industries ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace applications.
Understanding the Fundamental Design of Pogopin Connectors
Spring-Loaded Mechanism and Core Components
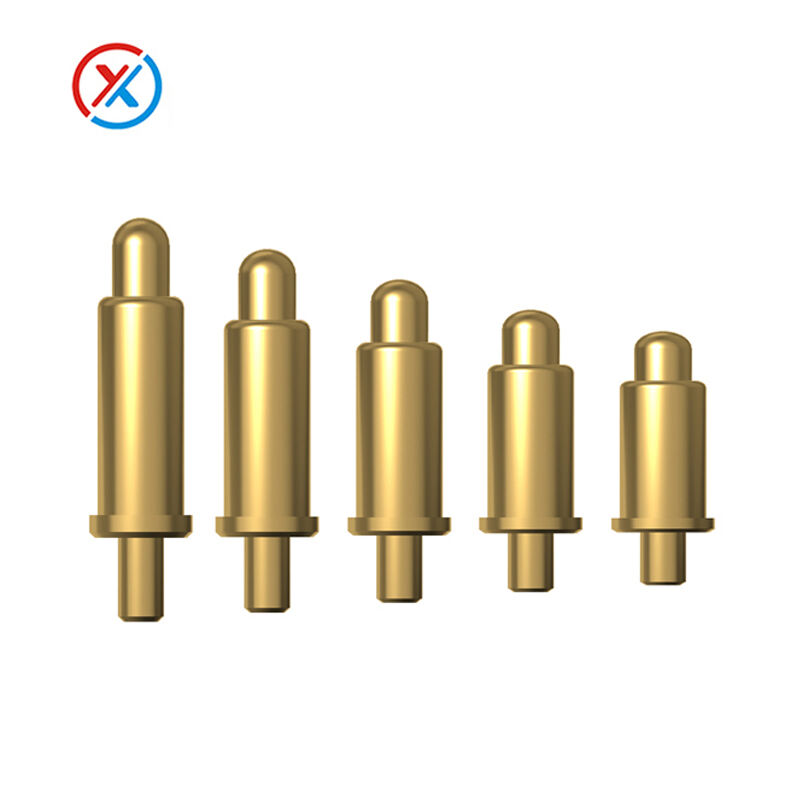
The pogopin derives its name from the spring-loaded mechanism that creates its distinctive bouncing action, similar to a pogo stick. This connector consists of three primary components: a precision-machined barrel, a spring-loaded plunger, and a contact tip. The barrel serves as the housing that maintains alignment and provides structural integrity, while the internal spring ensures consistent contact pressure against mating surfaces. The plunger moves freely within the barrel, allowing the pogopin to accommodate varying board thicknesses and surface irregularities while maintaining electrical continuity.
Manufacturing precision plays a crucial role in pogopin performance, with tolerances typically measured in hundredths of millimeters. The spring mechanism must provide adequate force to ensure reliable contact without causing damage to delicate circuit board surfaces. Premium pogopin designs incorporate gold-plated contact surfaces to minimize oxidation and ensure long-term reliability, especially in applications requiring thousands of connection cycles.

Material Selection and Engineering Considerations
Modern pogopin construction utilizes carefully selected materials optimized for electrical conductivity, mechanical durability, and corrosion resistance. The barrel typically consists of brass or phosphor bronze, chosen for their excellent electrical properties and machinability. Spring materials range from music wire to specialized alloys designed to maintain consistent force characteristics over millions of compression cycles. Contact tips often feature gold plating over a nickel barrier layer, providing superior conductivity while preventing migration of base metals.
Environmental considerations significantly influence material selection, particularly for outdoor or industrial applications. Some pogopin variants incorporate specialized coatings or utilize corrosion-resistant alloys to withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. The engineering challenge lies in balancing electrical performance, mechanical reliability, and cost-effectiveness while meeting specific application requirements.
Applications and Use Cases in Modern Electronics
Testing and Programming Solutions
The pogopin has become indispensable in electronics manufacturing, particularly for in-circuit testing and device programming. Test fixtures utilizing arrays of pogopin connectors enable simultaneous contact with multiple test points on populated circuit boards, dramatically reducing testing time compared to traditional probe methods. These spring-loaded connectors accommodate normal manufacturing tolerances in board thickness and component placement while ensuring reliable electrical connections during automated testing procedures.
Programming applications benefit significantly from pogopin technology, particularly when dealing with products that require firmware updates or calibration during production. The temporary nature of the connection eliminates the need for permanent programming headers, reducing both component costs and board real estate requirements. This approach proves especially valuable in miniaturized devices where space constraints make traditional connector solutions impractical.
Charging and Power Delivery Systems
Consumer electronics increasingly rely on pogopin technology for charging solutions, particularly in wearable devices, smartphones, and wireless accessories. These connectors offer several advantages over traditional charging ports, including improved water resistance, reduced mechanical wear, and simplified device sealing. The spring-loaded mechanism compensates for alignment variations between the device and charging cradle, ensuring reliable power delivery without requiring precise positioning.
High-current pogopin designs support rapid charging protocols while maintaining thermal management through specialized contact geometries and materials. Multiple parallel connections distribute current load, reducing individual contact stress and improving overall system reliability. This technology has enabled the development of wireless charging accessories that combine magnetic alignment with direct electrical connection, offering the convenience of wireless systems with the efficiency of wired charging.
Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
Electrical Characteristics and Current Handling
Pogopin electrical specifications vary significantly based on design requirements and intended applications. Standard test pogopin variants typically handle currents ranging from 100 milliamps to several amperes, with voltage ratings extending from low-level signals to hundreds of volts. Contact resistance represents a critical parameter, with high-quality pogopin connectors achieving milliohm-level resistance through optimized contact geometries and premium plating materials.
Signal integrity considerations become paramount in high-frequency applications, where pogopin impedance characteristics must match system requirements. Specialized RF pogopin designs incorporate controlled impedance features, including precision-machined geometries and specialized dielectric materials. These connectors maintain signal fidelity across frequency ranges extending into gigahertz territory, enabling their use in wireless communication systems and high-speed digital applications.
Mechanical Durability and Life Cycle Performance
Mechanical reliability distinguishes premium pogopin products from basic alternatives, with cycle life ratings ranging from thousands to millions of operations. Spring fatigue represents the primary limiting factor, influenced by compression ratio, material properties, and operating environment. Advanced pogopin designs incorporate optimized spring geometries and heat treatment processes to maximize operational life while maintaining consistent force characteristics.
Force specifications require careful balancing between contact reliability and potential damage to mating surfaces. Typical pogopin contact forces range from 50 grams to several hundred grams, depending on application requirements and contact area. Higher forces generally improve electrical reliability but may cause indentation or damage to soft contact surfaces, particularly on flexible circuit boards or gold-plated test pads.
Design Integration and Implementation Strategies
Mechanical Mounting and Alignment Systems
Successful pogopin implementation requires careful attention to mechanical design details, particularly regarding mounting methods and alignment accuracy. Press-fit mounting represents the most common installation approach, utilizing precision-machined holes in test fixtures or circuit boards. The interference fit must provide adequate retention force while avoiding excessive installation stress that could damage the pogopin barrel or surrounding materials.
Alignment systems become critical in multi-contact applications, where arrays of pogopin connectors must simultaneously engage multiple target pads. Guided alignment mechanisms, including precision-machined bushings and alignment pins, ensure consistent positioning and prevent side-loading that could cause premature wear. Some advanced systems incorporate spring-loaded mounting platforms that distribute contact forces evenly across the entire pogopin array.
Thermal Management and Environmental Protection
Thermal considerations significantly impact pogopin performance and longevity, particularly in high-current applications where resistive heating occurs at contact interfaces. Heat dissipation strategies include enlarged contact areas, enhanced material thermal conductivity, and integration with heat-sinking structures. Temperature cycling effects on spring properties and contact plating integrity require evaluation during the design phase to ensure long-term reliability.
Environmental protection measures vary based on application requirements, ranging from basic dust covers to hermetic sealing systems. Ingress protection ratings guide selection of appropriate sealing methods, particularly for outdoor or industrial applications. Some pogopin designs incorporate self-cleaning contact surfaces that remove oxide buildup and contamination through mechanical action during engagement and disengagement cycles.
Quality Considerations and Selection Criteria
Manufacturing Standards and Testing Protocols
Quality assessment of pogopin connectors involves comprehensive testing protocols that evaluate both electrical and mechanical performance parameters. Electrical testing encompasses contact resistance measurement, current carrying capacity verification, and insulation resistance evaluation under various environmental conditions. Mechanical testing includes cycle life evaluation, force measurement, and dimensional accuracy verification to ensure consistent performance throughout the operational envelope.
Manufacturing standards vary among suppliers, with premium manufacturers implementing statistical process control and comprehensive quality management systems. Incoming material inspection, in-process monitoring, and final product testing ensure consistent pogopin performance and reliability. Traceability systems enable rapid identification and resolution of quality issues while supporting continuous improvement initiatives.
Application-Specific Selection Guidelines
Proper pogopin selection requires careful evaluation of application-specific requirements, including electrical specifications, mechanical constraints, and environmental conditions. Current carrying capacity must accommodate not only steady-state requirements but also transient conditions such as inrush currents during device startup. Voltage ratings should include appropriate safety margins for overvoltage conditions and altitude derating factors.
Mechanical specifications including contact force, travel distance, and mounting requirements must align with mating component capabilities and fixture design constraints. Environmental factors such as temperature range, humidity exposure, and chemical compatibility influence material selection and protective coating requirements. Cost considerations must balance initial component expense against long-term reliability and maintenance requirements.
FAQ
What is the typical lifespan of a pogopin connector in regular use
The operational lifespan of a pogopin connector varies significantly based on design quality, operating conditions, and application requirements. Standard commercial-grade pogopin connectors typically provide reliable operation for 10,000 to 50,000 cycles under normal conditions. Premium industrial-grade variants can achieve cycle life ratings exceeding 1 million operations through optimized spring materials, precision manufacturing, and specialized surface treatments. Factors affecting longevity include contact force settings, environmental exposure, current levels, and maintenance practices.
How do pogopin connectors maintain electrical contact reliability over time
Pogopin connectors maintain electrical contact reliability through several mechanisms, primarily the constant spring force that ensures intimate contact between mating surfaces. The spring-loaded plunger automatically compensates for surface oxidation, wear, and contamination by maintaining consistent contact pressure. Gold plating on contact surfaces provides excellent corrosion resistance and low contact resistance, while the mechanical wiping action during engagement helps remove surface contaminants. Regular cycling can actually improve contact reliability by preventing the buildup of oxidation layers.
Can pogopin connectors handle high-frequency signals effectively
Modern pogopin designs can effectively handle high-frequency signals through careful attention to impedance control and signal integrity considerations. Specialized RF pogopin variants incorporate controlled impedance features, including precision-machined geometries and optimized dielectric materials that maintain signal fidelity at frequencies extending into the gigahertz range. Ground plane integration and coaxial configurations help minimize signal degradation and crosstalk in demanding applications. However, traditional test pogopin designs may exhibit impedance discontinuities that limit their effectiveness in high-frequency applications.
What factors should be considered when selecting pogopin connectors for a specific application
Selecting appropriate pogopin connectors requires evaluation of multiple factors including electrical specifications such as current carrying capacity, voltage rating, and signal frequency requirements. Mechanical considerations encompass contact force requirements, travel distance, mounting method, and expected cycle life. Environmental factors including temperature range, humidity exposure, chemical compatibility, and ingress protection requirements influence material selection and protective coatings. Cost considerations must balance initial component expense against long-term reliability, maintenance requirements, and potential failure costs in the target application.
Hot News
-
Challenges for Pogo pin manufacturers in the AI era
2023-12-14
-
Teach you how to understand Pogo pin spline structure
2023-12-14
-
What products can Pogo pin be used in?
2023-12-14
-
How to choose Pogo pin connector
2023-12-14

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 SR
SR
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 SW
SW
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 IS
IS
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 NE
NE





